- AI recruiting uses artificial intelligence to help companies reduce or automate tedious tasks in the recruitment process.
- Organizations primarily use AI in recruitment to help source candidates, screen applicants, schedule interviews, predict recruitment outcomes, and streamline the candidate experience.
- Despite skepticism surrounding AI technology, its ability to save time and offload tedious tasks can help companies develop more effective recruitment teams and discover quality talent faster.
Feb 11, 2025: Alana Rudder added a section differentiating machine learning and artificial intelligence, expanded the discussions on the use of AI in onboarding and its benefits, and highlighted current concerns surrounding AI technology in recruitment. She also added sections about AI recruiting tools and frequently asked questions.
How is AI used in recruiting
Recruiters use artificial intelligence (AI), such as machine learning, to help reduce or automate time-consuming tasks during the hiring process. It can also assist recruiters by sourcing, screening, and organizing applicants at the top of the hiring funnel.
Typically, companies can use AI to augment their recruitment strategies in the following instances:
- Candidate sourcing.
- Applicant screening.
- Interview assistance.
- Predictive analytics.
- Recruitment chatbots.
Many recruitment software solutions already include several of these AI elements. Understanding where and how to use AI in these tools can help companies acquire talent faster.
Candidate sourcing
AI-powered candidate sourcing features help recruitment teams speed up top-of-funnel hiring processes. Where it once took recruitment teams ages to craft job ads and manually post to various online job boards or social media sites, AI can now automatically handle these tasks.
Besides saving recruiters time, AI embedded in recruitment tools and job boards can make candidate sourcing more intentional. ZipRecruiter’s AI, for example, identifies the main attributes of a job ad, scans its database of thousands of résumés, and invites qualified candidates to apply.
Other AI tools can help make candidate sourcing more diversified while mitigating unconscious bias. For example, HireEZ’s outbound recruiting tool uses AI to scan millions of profiles and pinpoint individuals from underrepresented or minority groups that meet the job ad’s requirements.
On the backend, HireEZ masks candidates’ profile names, images, addresses, and schools so recruiters can focus on only contacting candidates whose skills best match the job description.
Watch this video to learn more about HireEZ:
Intelligent candidate sourcing tools can:
- Automatically distribute job ads across the internet, including to industry-specific sites.
- Target suitable candidates and invite them to apply.
- Promote diversity objectives by marketing jobs on sites for women, veterans, LGBTQIA+, people of color, people with disabilities, or other under-represented groups.
- Accommodate blind hiring initiatives.
Applicant screening
The primary function of AI in applicant screening is to help recruiters quickly sort candidates and identify top contenders. Applicant screening is one of the most time-consuming recruitment steps, according to a 2020 Yello survey, so implementing AI tools in this stage can drastically improve time-to-hire and other recruitment metrics.
For instance, AI can automatically disqualify candidates if they do not meet pre-determined screening requirements, screen résumés for experience related to the open role, and rank candidates with the most promise. This way, recruiters can spend more time evaluating candidates farther down the recruitment funnel.
However, companies should be wary of depending solely on AI tools for candidate evaluation. The legal landscape around these tools is evolving, and AI can reflect our human biases. To prevent a fate similar to Amazon’s AI recruiting tool and avoid the risk of developing homogenous workforces, companies should monitor their applicant screening AI and periodically review disqualified candidates for problematic patterns.
Applicant screening AI can:
- Parse resumes and rank top candidates.
- Disqualify or hide candidates who do not satisfy baseline requirements.
- Use applicant tracking systems (ATS) or HR software datasets to identify ideal candidates and automatically engage passive candidates.
- Automatically send and grade pre-employment assessments or other screening elements of top candidates.
Interview assistance
AI helps optimize the interview experience for candidates and interviewers through scheduling and note-taking features.
First, automating interview scheduling can significantly reduce the back-and-forth between recruiters and prospects to find the best interview time. LeverTRM, for example, emails interview stakeholders’ availability to candidates so they can pick the best time. The chosen time is then synced across everyone’s Google or Microsoft 365 calendars.
Learn more about LeverTRM’s interview scheduling tools in this video:
AI also allows recruiters to hold more productive and meaningful conversations. For example, generative AI tools like ChatGPT can prepare interview questions based on job descriptions beforehand. Meanwhile, other tools like Otter record, transcribe, and produce key takeaways from interviews so recruiters and hiring managers can focus on getting to know the candidates rather than taking notes.
Interview assistance AI can:
- Automatically schedule candidate interviews and sync them across calendars.
- Transcribe meetings and develop essential insights.
- Help prepare relevant interview questions.
- Assist recruiters in identifying fraudsters, including the use of deepfakes.
Predictive analytics
Predictive analytics uses machine learning to analyze past and present candidate pipelines and HR software data to predict when particular actions will occur. As a result, companies can act quickly to improve their recruitment efficiency based on current predictions.
For instance, Greenhouse’s Predicts feature applies machine learning to historical data to determine when a company will make a job offer for an open role and when the new candidate will start. Companies can use this information to optimize their hiring processes and make better forecasts.
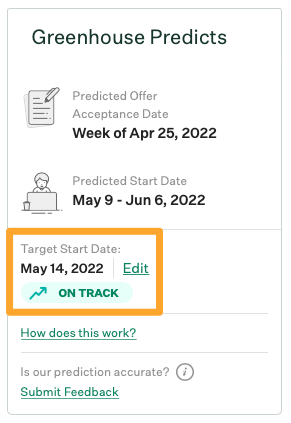
Additional predictive AI tools can notify recruiters when potential bottlenecks in recruitment processes will occur, provide accounting teams with forecasts on compensation spend, or even determine a new hire’s quality of hire before starting.
Predictive analytics should not serve as a company’s absolute source of truth as their predictions are not always accurate. Nevertheless, they are a great tool to assist recruiters in managing their time and provide hiring managers with realistic expectations of their job’s time-to-fill.
Predictive analytics AI can:
- Predict completion dates of different stages of the recruitment pipeline.
- Forecast recruitment and new hire budget spending depending on internal and external compensation and benefits data.
- Determine new hire ramp-up times and identify a new hire’s quality of hire.
Greenhouse is one of our favorite ATS solutions—learn more about its top features in our Lever vs. Greenhouse Comparison.
Recruiting chatbots
Recruiting chatbots are AI messaging tools that use natural language processing to answer candidate questions, commonly at the top of the hiring funnel. Although marketed as a tool to improve a candidate’s recruitment experience, chatbots give recruiters and hiring managers more time for other priorities by fielding common questions or requests.
Companies typically implement chatbots on their career sites to provide prospects with answers to questions like available jobs, required skill sets, compensation and benefits, or steps in the hiring process. Jobvite’s chatbot functionality, for instance, can guide prospects through an application process by collecting contact information and resumes, screening applicants, and scheduling interviews.
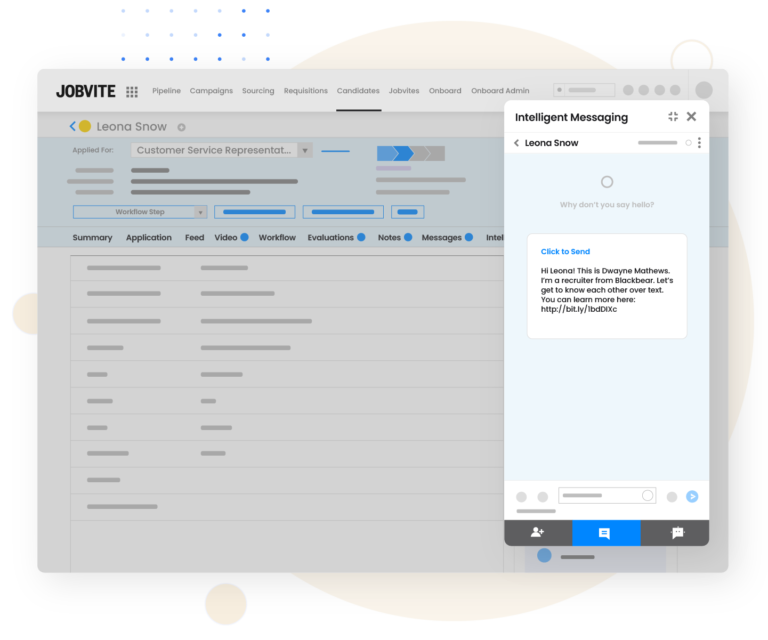
Text-to-apply chatbots function similarly by directing applicants to career sites or collecting required application data through text. As a result, chatbots make it easier for candidates to apply and improve recruitment departments’ overall candidate conversion rates.
AI recruitment chatbots can:
- Answer candidate questions on open positions and help them apply.
- Screen applicants for the position and schedule interviews.
- Facilitate text-to-apply campaigns.
- Remind candidates to finish their applications if they start and stop.
Onboarding
In the onboarding process, AI can improve efficiencies across multiple candidate touch points, from new hire document management during preboarding to feedback gathering, post-onboarding support, and training enrollment. For example, companies can use AI-powered software to automatically respond to new hire questions about onboarding paperwork.
AI onboarding tools can:
- Automate workflows such as onboarding document management and form completion.
- Integrate new hire onboarding data into the entire company tech stack.
- Gather feedback on candidates’ onboarding experiences and quickly summarize it into key points HR leaders can use to improve the process.
- Create personalized learning pathways for new hire skills gaps to help them succeed from their first day on the job.
Benefits of AI recruiting
As AI rapidly develops new use cases and capabilities, many businesses embrace its benefits in recruiting:
AI can help prevent recruiters from focusing on the small yet necessary tasks involved in hiring, such as automating email drip campaigns, writing job descriptions, posting job ads, or pre-screening applicants. Offloading these tasks can give time back to recruitment teams to concentrate on improving candidate experiences and enticing top contenders.
AI tools can work when recruiters cannot. Behind the scenes, AI is marketing job roles, answering candidate questions, assisting in applications, and engaging passive candidates 24/7 as needed. AI can maintain the baseline health of a candidate pipeline as recruitment assistants so recruiters can attend to more value-added hiring tasks.
In a survey conducted by Aptitude Research, half of surveyed candidates said they would appreciate the role of AI in their candidate journey, and over 60% said it would make the process more human. This may be partly because 65% of candidates report not receiving consistent enough communication during the candidate process, a problem AI can help solve.
AI automates lots of processes to improve candidate experience. This includes screening, ranking, communicating, scheduling interviews, creating appropriate questions, and assessing candidates. For example, to solve the inconsistent communication problem cited by many candidates, recruiters have said one of the most positively impactful recruiting capabilities of AI is its conversational and voice AI. You can use this technology to create personalized responses to candidates’ voice or text-based inquiries immediately and knowledgeably.
In multiple ways, using AI in the recruiting and talent sourcing process can improve your ultimate quality of hires. For example, AI can screen your business to understand what skills your company needs based on the gaps in your workforce. It can then suggest candidates who are strong in those missing skill sets.
It may seem daunting to have to pay for the purchase of a new business technology, let alone the labor time in training employees to use it. However, in the end, most companies find AI’s implementation saves them money.
Aptitude Research found it can drastically cut down on elements of the recruiting process, leading to an overall 35% reduction in costs associated with hiring. In addition, it can boost the quality of hire by 52%, meaning companies are less likely to have to pay for a repeat recruiting process for the same position in the near future.
Challenges of AI recruiting
Some challenges have posed risks to small businesses looking to implement AI into their work processes. However, recently, many of these challenges have been met by solutions as AI “grows up.” In this section, we explore challenges—such as transparency laws, workforce hesitancy, and loss of human interactions—and the advances and learned best practices that are helping to solve these challenges.
As scrutiny around AI intensifies, so do regulations on its proper and ethical use. New York City, Maryland, and Illinois have enacted legislation regulating AI in screening, facial recognition, and interview videos. Companies should investigate the laws in their states and localities. Still, it is always a good idea to remain transparent with candidates on AI use and thoroughly vet how vendor AI tools make decisions.
While many recruiters are excited about how AI can automate tedious, high-volume tasks, others are skeptical of adopting the new technology. Aptitude Research found that hesitation primarily revolves around gaps in understanding how AI works and its usage (53%), concerns with introducing bias into HR processes (43%), lack of workforce readiness (38%), and an untrusting attitude toward vendor value propositions (27%).
However, year after year, as recruiters and candidates are learning more about the benefits of AI, they are more willing to embrace it. In the same survey, candidates reported that businesses are extensively using AI to improve:
- Interview scheduling and management (27%).
- New hire onboarding (25%).
- Talent matching and sourcing (22.5%).
- Talent assessment counting (22.5%).
The fear of loss of human contact is a genuine challenge with AI. Chatbots, for instance, aren’t a true substitute for human beings who can pick up the nuances of various questions.
However, AI can enhance your recruiting process. For example, AI can learn about the candidates going through your hiring pipeline and then offer personalized recommendations for them, creating a more responsive and personalized candidate experience. In doing so, it becomes a support to enhance the same personalized experiences candidates expect from people, just at a larger scale.
The happy medium: AI and human-centric recruiting
In a survey of 950 businesses, 56.8% of respondents reported that their happy medium when using AI in recruiting is to leave the final candidate decision up to humans and lean on AI as a supportive tool only. These companies believe that removing people from the recruiting process altogether would be a mistake, but using AI to enhance the recruiter’s efforts is not.
For example, recruiters can use AI to match candidates to roles in which they’re likely to succeed. Recruiters can then move forward with candidates they’re most interested in. This way, they invest more time with fewer but more high-quality candidates. The result is a more personalized and fair approach to fostering a positive candidate journey.
AI predictions can also help to inform which candidate will most succeed on the job once they have reached the top of the funnel. In turn, recruiters can set up new hires for success by selecting those most likely to succeed. Overall, a successful candidate creates a more satisfactory experience, one that is likely to result in more employee referrals and retention.
Does AI create bias?
Over 40% of companies are concerned about how AI bias may impact the HR process. In the context of HR, however, bias can often be avoided when AI is used in the recruiting process but only if it is correctly implemented. In fact, in many cases, it can reduce bias.
Companies should be aware of how AI can reduce and promote recruitment bias. Just as AI can mitigate our biases by hiding candidate demographics, it can just as easily designate a demographic as better suited for a job simply because of past or present employees’ backgrounds.
Remember: AI does not intend to be biased. Any outward bias AI demonstrates merely reflects the data we provide it. However, allowing AI to access more diverse data sets and proactively placing parameters on its decision-making abilities can train it to be fairer and more equitable than us.
The business impact of AI recruiting
Recruiters are using AI to improve efficiencies in their candidate sourcing, screening, job matching, job training, decision-making, and other essential recruiting and hiring workflows. Increasingly, recruiters who don’t lean on AI to handle some tasks for them will not have the same freedom as AI-leaning competitors to focus on the more nuanced components of hiring that only a human can do well. In the end, this means they lose the competitive edge that is the human touch at all the right touch points in the candidate journey. Candidates will simply move on to another company that can better value them.
If you and your team are ready to make the AI in recruitment leap, browse our Recruiting Software Guide for the top solutions to fit your needs.
AI recruiting tools
Today’s HR tools are increasingly embracing AI to help companies create efficiencies and reach goals. It does so by implementing the technology into talent sourcing, evaluation and selection, onboarding, and new hire learning development processes.
Rippling, for example, incorporates AI into its talent sourcing, recruiting, interviewing, candidate evaluation, talent selection, and candidate feedback processes. This way, AI helps client companies build competitive workforces from talent sourcing to new hire learning and development processes.
Frequently asked questions (FAQs)
You can use AI to both automate repetitive tasks and create a personalized recruiting experience for job candidates. For example, many recruiters use AI to:
- More efficiently source candidates from an equitable array of talent pools.
- Screen candidates.
- Answer candidate questions.
- Communicate with candidates at high-value touch points in their journeys.
- Match candidates to the roles in which they’re most likely to succeed.
- Select from among equally qualified candidates based on their aptitude for the role.
- Save time in common recruiting and onboarding workflows.
- Place candidates in the best developmental programs once they’ve been onboarded.
Not only is AI the future of recruitment, but it is already forming competitive advantages for many companies by helping them create a positive candidate experience that continually attracts top talent. As such, its value to companies is growing rapidly and, by 2030, is projected to turn recruitment AI into a $942.3 million market, according to FnF Research. In addition, these Workable statistics show rapid growth in using AI adoption in recruiting:
- Two-thirds of businesses surveyed by Workable envision increasing their AI usage in hiring in the next five years.
- 26.8% of those companies see the use of AI in hiring increasing substantially in the next five years.
- 41.3% of surveyed businesses believe they will increase the use of AI slightly within the next five years.
In summary, 67% of surveyed businesses expect to increase their AI usage in hiring in the next five years. And only 5.8% of surveyed companies expected a decrease in its usage in the next five years. But while the future of AI recruitment involves AI, it likely won’t replace human recruiters anytime soon.
Mastercard implemented AI in their recruiting process, from talent scouting and engaging candidates to interviewing top candidates. In doing so, it increased its talent community from under 100,000 candidates to over one million. Other companies that incorporated AI into their recruitment processes include Stanford Health Care, IBM Watson, Hilton, Amazon, Delta Air Lines, Unilever, and Procter and Gamble (P&G).
Companies use AI to create efficiencies throughout their HR processes. For example, many use the technology to manage workforces, automate administrative tasks, develop constructive performance reviews, ensure employee and company compliance, and develop improved learning and career development pathways for employees.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are intrinsically connected, with ML being a subset of the overarching AI technology. While AI is the development of computer systems that perform tasks that are often left to human intelligence, ML uses algorithms and statistical models to look for patterns in data. ML is used as a component technology to create AI systems.
In the context of recruiting, they are often used in conjunction. For example, you can use machine learning to help candidates surface jobs they’re suited for using an algorithm. Then, recruiters use AI to summarize key points in a candidate’s interview, helping them make faster hiring decisions.
Learn more: AI in HR: 6 Ways Artificial Intelligence Impacts the Workplace





