Key takeaways
Take a look at our software guides for benefits administration and global payroll to browse tools that support your international employees.
What are global employee benefits?
Benefits are a type of indirect compensation an employer offers in addition to an employee’s direct, financial compensation. Employers use benefits to attract and retain employees, promote employee happiness and well-being, and foster company loyalty.
In fact, MetLife’s 2022 U.S. Employee Benefit Trends Study found that 66% of employees say a comprehensive benefits package is a must-have.
For a company deciding to move into the international space, though, global benefits look entirely different compared to those offered by companies in the United States. Constructing and executing an effective strategy requires determination and a willingness to adapt to different cultures and requirements.
“You need to be aware of the norms in each country you enter,” says Amy Spurling, CEO and founder of Compt, an international and remote employee perks and rewards software. “Normalizing to the U.S. will not work. Period.” U.S.-based employers must consider not only the local laws of their international employees but also the culture and the expectations employees have of their employers in each region.
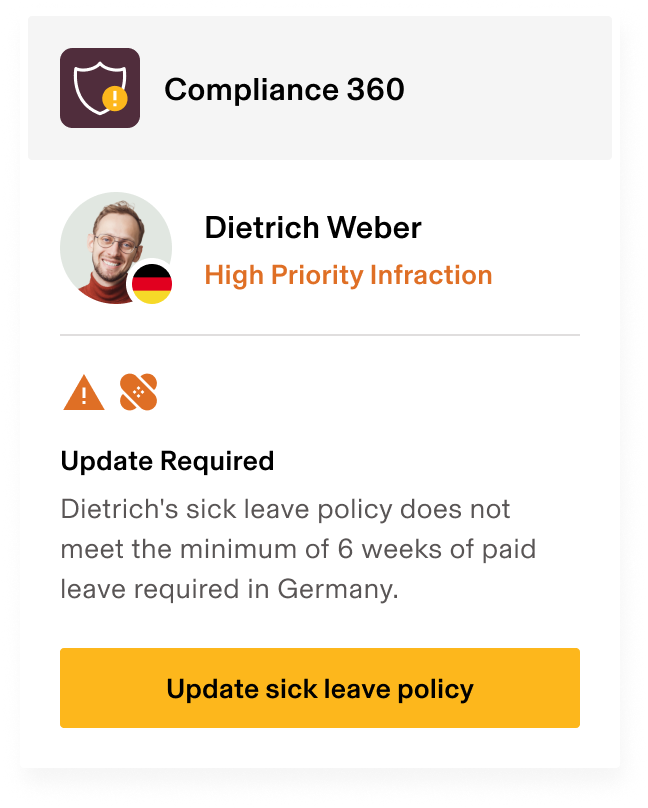
For example, an employer with employees in Brazil must offer a vacation bonus worth one-third of an employee’s monthly salary after a year of work. Though the logistics of administering these benefits might seem relatively straightforward, it’s important to consider the broader impact:
Thus, offering global benefits requires HR teams to navigate various logistical obstacles, negotiate with international vendors, and adhere to local customs to provide compliant and appealing benefits to their international employees.
What is a global benefits strategy?
A global benefits strategy is a plan that employers follow when implementing a benefits program for their employees on a worldwide scale. For the strategy to be successful, employers must offer benefits both compliant with international regulations and enticing to their employees.
A global benefits strategy looks different from one company to the next. Some may take a use-case approach that standardizes the benefits from the most generous locality to all of their employees to remain fair. Others use company values or goals to guide what benefits they offer employees locally.
However, companies should avoid a one-size-fits-all approach.
“That’s very much a losing strategy,” says Spurling. “There are different costs of living. There are different compulsory benefits. So (companies need to take) it to (a) value place rather than trying to make everything exactly the same.”
For companies to compete in the global space, their benefit plans should be equitable. Equitable company benefit programs ensure employees enjoy a standard of living equivalent to their peers, regardless of their geographical location.
Elements of a global benefits strategy
Benefits change from country to country and even between provinces and other localities in each country. However, the elements of a global benefits strategy include government-provided benefits, government-mandated benefits, and voluntary employee benefits.
How to create a global benefits strategy
For new companies just branching out internationally, the steps below provide the foundation for a global benefits strategy that aligns company values with relevant and attractive employee benefits.
1. Define the budget and strategy
Spurling argues that understanding the company’s budget is the first step in an effective global benefits strategy. Because benefits are not just country-specific but region or locality-specific, companies need to estimate the costs of government-mandated benefits and balance those against any supplementary or fringe benefits they would like to offer.
Additional costs could include those for third-party administration, in-house staff, or global payroll or benefits administration software. Companies particularly concerned with their budgets may invest in stipend programs or multinational pooling strategies to lower costs. However, once companies have their numbers in place, they can begin to narrow down their strategy.
To Spurling, a winning global strategy is a balance between the company’s budget and culture. She wants companies to ask themselves, “What do we believe? What’s important to us? Is it family? Is it wellness? (Is it) supporting mental health, preventing burnout, or building a more diverse team?”
Once companies understand what is important to them and their employees, they can begin regionalizing.
2. Understand the laws
Global benefits are about adhering to tax laws in various countries and protecting employees’ civil liberties. Therefore, companies must research national and local laws before implementing their benefits programs. Failing to understand the local laws in other countries sets companies up not only for severe fines or penalties but can also negatively affect the company’s reputation and status in the international market.
3. Accommodate cultural differences
Companies must also understand a country’s cultural differences when implementing their global benefits strategy. A valuable benefit in one country may seem like the bare minimum or illogical in other countries and cultures.
For instance, a gym membership subscription may seem like an excellent perk to employees in urban areas but is utterly impractical to those who live miles away from health clubs. Companies should always check with their employees or local sources before starting their benefits programs; otherwise, providing the wrong benefits could make a company seem culturally insensitive, damage its reputation, or stall hiring efforts.
4. Conduct a competitor analysis
Companies must compare their benefit offerings directly with their competitors in the region. While a market analysis of typical benefit offerings establishes a baseline, offering benefits that meet or exceed those of their competitors ensures a steady stream of new talent while reducing turnover risk. Moreover, robust benefit offerings help companies promote their global brand positively, attracting new employees and customers alike.
5. Consider outsourcing benefits
Partnering with experts to help administer or develop a global benefits program can help companies break into the international sphere. Professional employer organizations (PEOs) and employers of record (EORs) are two options companies can consider.
Although their approaches differ, both options employ international companies’ workers directly to mitigate risk. In addition, EORs and PEOs handle the administrative tasks associated with employee upkeep — such as offering competitive and relevant benefits — so companies can return their focus to primary business objectives.
One drawback, however, is cost. EORs and PEOs work for smaller companies with a small international workforce. However, as businesses scale and their administrative resources grow, the more cost-effective option is self-administering global payroll and benefits.
6. Leverage software to help
Unless they are outsourcing benefits administration, companies should consider a global payroll or benefits administration software solution to simplify the implementation of their global benefits strategy.
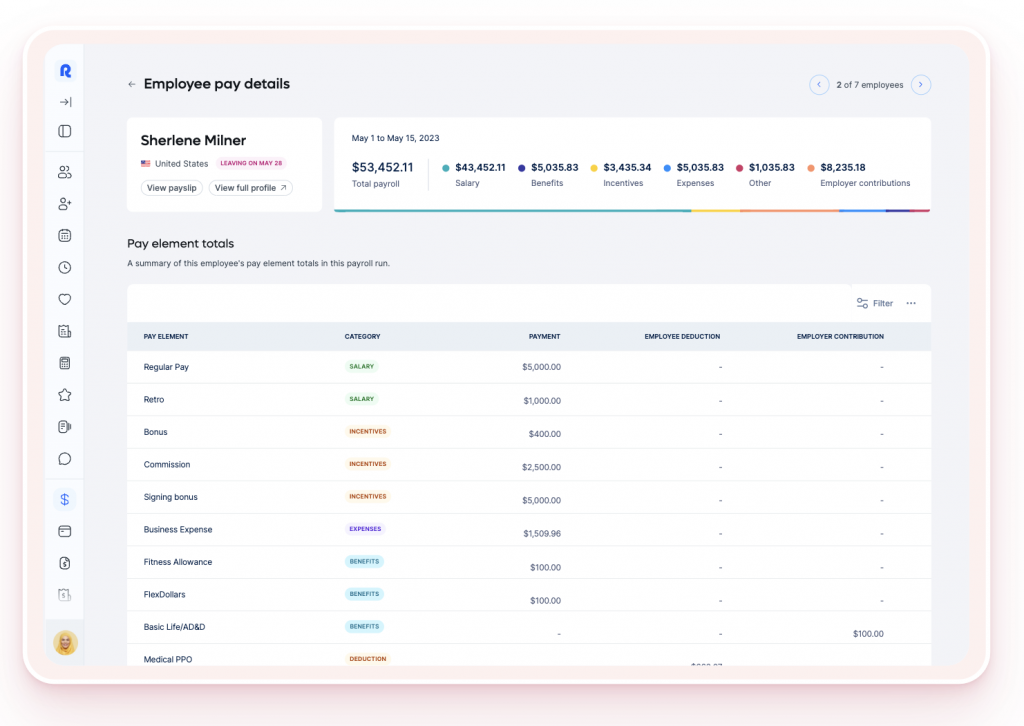
Companies can add tactical global software solutions to their HR tech stacks or upgrade their existing software to its international equivalents. Rippling, for example, integrates payroll and benefits administration in one system that changes the required employee documentation depending on where the employee lives.
Remote, on the other hand, offers curated local plans to reduce the time companies have to spend researching valuable country-specific benefits. Additionally, Remote’s API allows its platform to integrate with a company’s current HR software, so employers don’t have to sacrifice their existing tech to move into the international space.
Also read: 7 Questions to Consider Before Choosing a Benefits Administration System
7. Communicate the logistics and execute the strategy
Creating a global benefits strategy requires collaboration among executives, HR teams, accounting departments, payroll specialists, and legal experts. However, once it is finalized, companies must communicate and execute the global benefits strategy among their international teams and ensure it is upheld consistently in each country.
This goes beyond notifying stakeholders of the strategy’s existence. Successful implementation also means making sure the infrastructure to support the plan is in place, such as international employee onboarding procedures and carrier billing setup.
8. Be flexible
Moving into an international market, especially for the first time, requires tenacity and adaptability. Companies will encounter situations that they cannot anticipate. However, by keeping their broader goals and the well-being of their employees in mind, pivoting or changing course can often lead to more cost-effective or valuable international employee benefits in the long run.
How a global benefits strategy can set a company apart
As companies hire for the first time in other countries, they must reconcile both their global compensation and benefits strategies. A benefits strategy is not only about providing government-mandated benefits but also:
As Spurling explains, a global benefits strategy is successful when “you talk to people, no matter where they’re from in the world, and you know which company they work for, in a positive way.” An effective global benefits strategy can set a company apart from other employers, paying dividends from now and into the future.
Administering a global benefits program can be complicated. Check out our benefits administration and global payroll software guides for tactical solutions to fit your business needs.