Key takeaways
Cloud analytics is a popular business intelligence tool because it can manipulate large datasets that help businesses improve decision-making. This article will cover cloud computing analytics, why it’s essential to successful businesses, and the pros and cons of this business intelligence tool.
What is cloud analytics?
Cloud analytics’ popularity is derived from its ability to provide businesses with a competitive edge by using sophisticated analytical algorithms applied to data stored in the cloud. Cloud analytics help businesses make quick and accurate decisions by analyzing large data sets to find patterns or trends that help managers make data-driven decisions.
Cloud-based data analytics is effective because it can combine data from different sources into one location and process structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data into a format easily interpreted by a human. Combining these different data sources gives businesses a holistic view of multiple data sources that can improve forecasted outcomes and decision-making.
Cloud analytics’ ability to improve decision-making by extracting new insights from various data sources helps businesses improve overall business operations and meet customer needs.
What are the types of cloud analytics?
The types of cloud analytics in the cloud refer to public, private, or hybrid cloud solutions and the cloud computing model a business decides to use. The cloud computing models are:
- Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS)
- Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS)
- Software-as-a-Service (SaaS)
Public cloud computing is when a third party provides computing services over the internet. A public cloud computing service is a multi-tenant architecture because multiple companies use the same resources. See Figure 1 for cloud computing models.
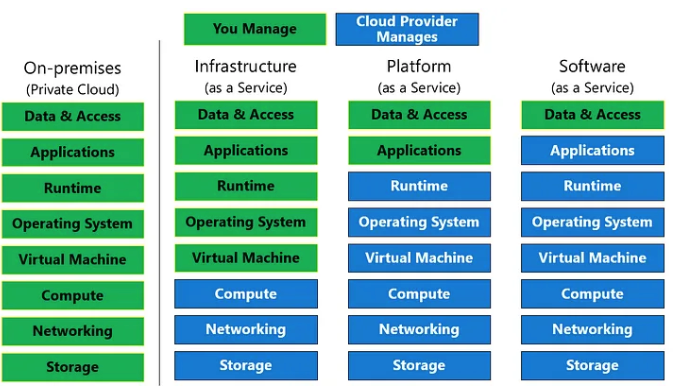
With a private cloud computing solution, the cloud computing resources are only available to one organization or business using the cloud services. Private clouds are also known as corporate clouds, and the organization using the resources is responsible for maintaining all the hardware, software, and data. A hybrid cloud computing solution combines public, private, or an on-premises data center. Businesses also need to consider the cloud computing model they will use.
Using an IaaS solution will require a business to support the Operating System (OS), middleware, data, and any applications with an internal IT staff. A PaaS solution requires a company to support the applications and data only, while the Cloud Service Provider (CSP) supports the OS and remaining software and hardware in this cloud computing model. The CSP fully supports the SaaS model, and the organization using it is responsible for data and access to the data.
Selecting a robust cloud analytics solution
Before you begin researching for a good BI solution with cloud analytics, create a list of the 5-7 features your business must have in a BI tool with cloud analytics. Get stakeholder input from personnel that will use the application or representatives from each department while ensuring you have a good mix of technical and non-technical staff participation from each department. Once you have input from all departments, create a selection team from the most enthusiastic members of the organization to evaluate BI solutions.
Business intelligence tools to consider:
- Microsoft Power BI – Best for existing Microsoft 365 users
- Zoho Analytics – Best low-cost BI solution with cloud analytics options
- Amazon QuickSight – Best for displaying data visualizations
- Salesforce Tableau – Best for performance and working with large data volumes
- Domo – Best for organizations with non-technical users due to being easy to learn
- Oracle Analytics – Best for data ingestion and modeling while increasing productivity in analytics-driven business environments
Industry-specific cloud analytic solutions
Specific business industries can select a cloud analytic vendor that caters to an industry-specific business need. For example, business industries such as healthcare, government, retail, or financial services can explore these industry-specific cloud analytic software solutions. Industry-specific cloud analytical solutions possess the same data modeling capabilities, Application Programming Interfaces (APIs), big data tools, and workflow resources.
However, the resources are designed and aligned to meet industry-specific requirements. The requirements range from meeting compliance regulations to key performance indicator (KPI) requirements.
Implementing a cloud analytics solution
An exemplary implementation plan begins with assessing your current business operations and the goals you want to attain once your cloud solution is implemented. What improvements does an organization want to gain, and is the organization prepared to go through a transition period during the implementation phase?
It is essential to assess which processes are critical to your business and when they should be migrated. Notifying your customers of the upcoming changes that may temporarily impact services and responsiveness will ultimately improve overall business operations and benefit customers, so customer notification is crucial.
Assessments are independent actions that each business needs to consider and prioritize the business operations or services provided to customers that least impact customer satisfaction and revenues during the implementation phase. The assessment also needs to consider the level of training required for employees to become effective users of a cloud analytical solution to avoid any impediments to business operations.
After the assessment, businesses must consider the cloud computing model and whether a public, private, or hybrid solution will be used. The cloud computing model a company will use determines if an information technology (IT) staff will remain or the CSP will manage their selected cloud solution.
EXPERT TIP
To ensure a business can successfully migrate to a cloud-based solution, the company should consider hiring a cloud migration specialist that provides the specialized experience needed to move to a cloud solution in the shortest time possible.
The cloud migration specialist can help make important migration decisions such as:
- Selecting which business process to move first.
- Taking advantage of the automation capabilities available using a cloud solution.
- Help create a cloud governance framework by ensuring the appropriate policies address security audits and user accountability issues.
- Three to six months of continual monitoring and optimization of the implemented BI cloud analytical solution.
What are the primary features of cloud analytics?
Cloud computing analytics use artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), deep learning applications, and mathematical and computational tools. These applications and mathematical tools create data and analytical models, including processing applications that generate insights for quicker decision-making. All cloud analytical solutions offer these standard functions:
- Data models visually represent data and the relationship between different data points.
- Analytical models allow users to understand complex datasets and predict the outcome of different business scenarios.
- Processing applications are used to process large datasets that present new insights for better decision-making.
Other features in cloud analytic solutions are a visual dashboard, embedded or augmented analytics, and alerting options that can be programmed and triggered when an event occurs.
Why is cloud analytics important in the business world today?
For any successful business that wants to remain competitive, cloud analytics allows businesses to stay relevant and competitive by uncovering trends or patterns and predicting outcomes that lead to better business decisions. Cloud analytics positively impacts businesses on multiple levels besides just improving decision-making. Cloud analytics improves business operations in the following ways:
- Lowering cost by using pay-as-you-go pricing and removing fixed expenses such as physical servers and software costs.
- Improved security in the CSP uses built-in security analytics that continually scans for suspicious activity and uses state-of-the-art encryption and cloud firewalls.
- Collaboration provides multiple methods for sharing data, including file sharing, concurrent editing, and dashboard sharing.
- Scalability allows businesses to use more or fewer CSP services depending on demand, and flexibility enables companies to adjust rapidly to meet business demands.
- Multiple storage options provide businesses with storage options and powerful computing resources, allowing organizations to analyze large datasets expeditiously.
Businesses that are required to operate on a 24/7 basis while using a SaaS cloud computing model will gain significant efficiencies in business operations with remote access from any location with an internet connection and a web browser.
Multiple communication methods are available, along with tangible benefits such as cost-effectiveness, enhanced security, and service level agreements (SLAs) for various services, including backups and data recovery. The other two cloud computing models will require some IT staff to remain on the payroll.
What are cloud analytics best practices?
A business’s proprietary data must always be protected, regardless of the cloud computing model selected. A must-have best practice requirement is always to ensure your data is encrypted end-to-end, whether the data is at rest, in transit, or being used in memory (i.e., RAM). End-to-end encryption ensures your data is always protected from unauthorized users.
Businesses can establish data protection policies, set limits on sharing data, and put procedures and policies in place to ensure data is never sent to an unmanaged device. Service-level agreements regarding data protection can clearly outline responsibilities between both entities.
Other best practice requirements for cloud computing analytics are:
Data governance
Establishes policies, rules, and processes covering data quality, protection, and security while ensuring the data is always reliable and available. The main components of data governance are people, processes, and technology. Each of these components requires clearly stated intentions of what are authorized actions and unauthorized actions.
Automation
Built-in automation can respond to events and changes without human intervention. Automation also eliminates manual processes that can introduce errors into cloud operations. Automation increases the speed of analytics, too.
Security monitoring
Security monitoring detects anomalies and prevents data loss, and the monitoring tools can enforce security policies and least privilege access. Security monitoring remediates security threats, mitigates potential damage, and reduces response time to a security incident. Use intrusion and prevention technology to help secure your business network.
Behavioral analytics
In addition to behavioral analytics having a role in security monitoring with anomaly and breach detection, behavioral analytics is used in marketing automation systems and customer relationship management applications by observing and analyzing customer responses. Behavioral analytics helps businesses understand their customers and anticipate their needs or identify any obstacles that may hinder a customer from purchasing.
Data analytics framework
Only use authorized tools within the analytics framework. Test and validate the available tools in the cloud-based data analytics framework.
Apply filters when appropriate
Filters are used to retrieve relevant data when executing a cloud analytical operation. In addition to retrieving relevant data only, businesses can save money by not retrieving data that doesn’t meet the intent of the user’s request. So, detailed parameters used in a filter lead to relevant data retrieval and cost savings by not retrieving extraneous data.
What are the benefits and drawbacks of cloud analytics?
Some benefits of cloud analytics have already been mentioned, such as improved security and decision-making. Here are some other tangible benefits of using cloud analytics:
Improved quality control
With data stored in a single location and format, the built-in file-sharing feature allows authorized personnel to access the most updated information, removing scenarios where one department uses outdated information to make decisions because the most updated information was in another department’s siloed application. Any updated information from any department is immediately updated when using Business Intelligence (BI) software with cloud analytic operations.
Streamlined business operations
Cloud analytics enhances an organization’s business intelligence processes, such as document analysis, which can uncover insights in unstructured data. Finding relevant information in unstructured data helps businesses make better data-driven decisions.
Improved mobility
A cloud-based BI solution allows authorized personnel to access cloud analytics tools from anywhere at any time with an internet connection and web browser. Mobile BI tools such as cloud analytics provide secure connections to access cloud-based data resources that emulate an employee physically being on the work site.
Enhanced document collaboration
Document collaboration in a cloud environment allows personnel to see any updates instantly in real-time, allowing for immediate feedback that promotes efficiency. Legal documents, contracts, or proposals requiring input from multiple personnel, regardless of location, will enable these documents to get done much quicker rather than go from person to person via a routing folder or attached in an email.
Automatic software updates
Instant software updates will minimize any potential zero-day attacks. Cloud business intelligence software automatically updates without the need for human intervention. Depending on the cloud computing model selected, a business may have to update an application or an OS.
Improved disaster recovery
There is always the potential for data loss from a cybersecurity threat or a hardware failure of on-premises equipment. Still, CSP has established SLAs that minimize downtime for any service outage. The best cloud service providers are proficient at data recovery because their geographically dispersed data centers make recovery fast and easy.
Using a BI cloud analytics platform offers a multitude of benefits that we already mentioned, like cost savings, scalability, flexibility, improved security, and improved overall business operations. The tangible benefits of cloud analytics make it an easy decision for any business wanting to remain competitive.
Drawbacks
The benefits are numerous when considering using a BI cloud analytics solution. Still, as with any product touted as beneficial, a BI cloud analytical solution has some drawbacks.
- Vendor lock-in: If a business is not happy with the CSP services, the company will have to remain with the CSP until the end of the contract.
- Data security: Businesses are always concerned about data security, so to minimize this concern, businesses can perform their security audit that is included as part of a signed SLA.
- Internet dependency: Chances are slim the internet will go down, but the success of your business is highly dependent on the availability of the internet and consistent internet connectivity.
- Cost overruns: Running unfiltered cloud analytics that retrieves useless or incorrect data can contribute to cost overruns.
- Connectivity issues: These can occur at any time, depending on an employee’s location.
- Limited flexibility and control: Businesses will not have the control or flexibility to meet a new requirement when using a CSP-supported application.
Cloud analytics is a helpful business intelligence tool that provides businesses with seamless communication options, efficient business operations, and multiple methods to improve the customer experience. Conversely, interested companies need to be aware of the potential drawbacks when using a cloud-based solution and the available options to counter any drawbacks that can be addressed in an SLA to minimize these potential pain points.
What skills are required to utilize cloud analytics?
Non-technical business users wanting to use cloud analytics can start by accessing user-friendly dashboards and reports that lead to better decision-making. Non-technical business users already possess communication and math skills, and some users may be familiar with statistics. Other helpful skills you’ll need are the following:
Statistics
Business users must understand statistics and probabilities to successfully use cloud analytics, including a refresher course on algebra and linear functions if required.
Database management knowledge
A fundamental knowledge of how databases operate and the purpose of primary and foreign keys is basic knowledge users must know. Business users must also understand the concept of database normalization to the third normal form.
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML)
Artificial intelligence plays an essential role in cloud analytics. Machine learning and deep learning are all sub-categories under AI, so users must understand AI’s role in cloud analytics and BI. AI-powered analytics help organizations forecast trends and anomalies in their data, and ML models are used to identify patterns and trends in large datasets.
Data analysis and visualization
Knowing how to collect, process, and analyze data is one of the core principles of cloud analytics. Another core principle is visually displaying the data in a manner easily understood by a target audience.
Next steps
Now that you have foundational information on cloud analytics and the role your organization must fulfill based on the cloud computing model selected, you can start formulating a checklist. What cloud analytical features are essential to your organization, and will your organization still require an IT staff? Will you require a BI implementation specialist to assist in the transition, and how long will the specialist be onsite? What training will be necessary for your non-technical users to become proficient in using cloud analytics tools? Important questions and priorities should be documented in a project charter and approved by a Chief Information Officer. Looking for the latest in Data Analysis solutions? Check out our Data Analysis Software Buyer’s Guide.