Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) trunking transforms landline-based private branch exchange (PBX) system into a digital phone network, allowing voice calls to travel via the internet instead of copper lines. This opens doors to scalable capacity based on call volume, reduced hardware costs, and access to advanced communication features.
SIP trunking explained
SIP trunking is a phone system setup made up of two key elements: SIP and trunking. To better understand its use, let’s first define what SIP and trunk mean on their own.
- SIP is a signaling protocol defining the rules for establishing, modifying, and terminating communication sessions between endpoints over an internet protocol (IP) network.
- Trunking refers to the process of combining multiple phone lines or communication channels into a single connection called a “trunk.”
SIP trunks provide voice-over-internet-protocol (VoIP) connectivity between an on-premise phone system and the public switched telephone network (PSTN). This enables businesses to enjoy VoIP and PSTN calling through their on-site PBX.
How does SIP trunking work? A step-by-step guide
SIP trunking works by sending and receiving communications over the internet through PBX. To give you a clearer idea about the definition of SIP trunk and how it works, let’s look at the three key requirements for its implementation.
- PBX system: A PBX infrastructure refers to your company’s private telephone network, connecting office phones to internal and external callers. It serves as the brain center of your business phone system and provides features for routing inbound and outbound calls.
- SIP provider: It refers to an internet telephony service provider (ITSP) offering SIP services such as voice calls, video conferencing, and virtual phone numbers. It connects your PBX to the PSTN to route a call to its destination.
- SIP trunk: The SIP trunk line is the digital version of an analog phone line that carries signals or packets of multimedia data such as voice, SMS, or video. A trunk may consist of up to 20 or more concurrent channels. It acts as the middleman between your company’s PBX and ITSP, allowing users to make and receive calls.
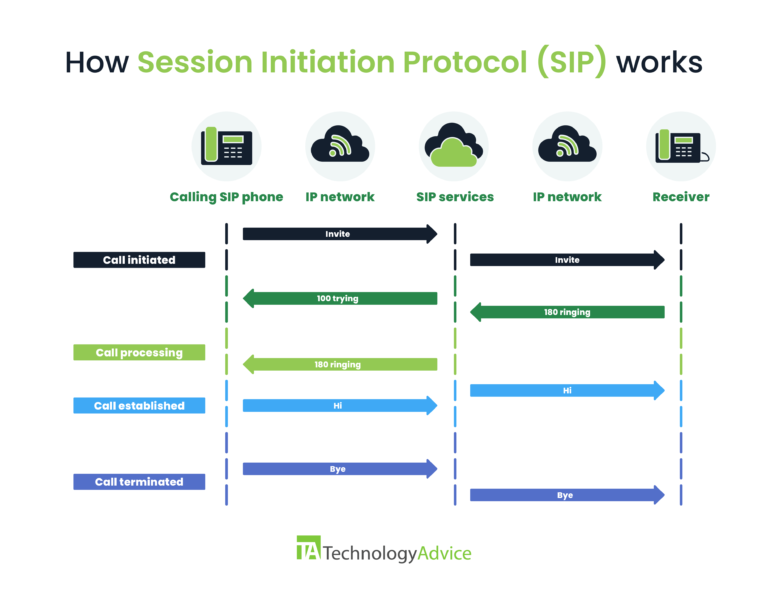
Let’s take a deep dive into how these components work together to enable SIP trunking.
Step #1: Call initiation
When a user initiates a call, the PBX system generates the SIP request and sends it to the SIP trunk provider. The SIP request contains an INVITE message that establishes a call session.
Step #2: Call processing
The SIP trunk provider identifies the destination of the call and routes it as follows:
- If the recipient uses a cloud-based phone, the call stays on the internet.
- If the recipient is on a traditional landline, the SIP trunk provider will connect to the PSTN, incurring carrier fees.
Step #3: Call transmission & management
After the call is established, the PBX will now convert the voice signal into digital packets using a codec to prepare for transmission. Once converted, the SIP trunk transmits the digital voice packets to the SIP provider over the internet. If the destination uses PSTN, the SIP provider converts the digital packets back into an analog phone signal before reaching the recipient.
As the call progresses, SIP manages the connection by maintaining proper call sequencing to ensure packets arrive in the correct order. It also facilitates the provision of other multimedia features such as call transfers, instant messaging, and video conferencing.
Step #4: Call termination
When the call ends, SIP ends the session by sending a termination (BYE) request. Once the other party acknowledges, the PBX will officially close the connection.
Top SIP trunking providers
Many unified communication providers offer SIP trunking as part of their broader cloud-based services. They vary based on pricing models, functionality, and redundancy options. To help you decide, we listed four industry-leading SIP trunking providers offering reliable connectivity, robust features, and competitive pricing.
SIP trunking providers
Monthly starting fee
Key features

RingCentral
Custom pricing
- Integrated contacts
- Flexible migration paths
- Available in over 50 countries

Nextiva
$14.95/user
- Detailed call records
- Fraud mitigation
- 100 call minutes included

Ooma
$19.99/user
- Advanced cloud call flows
- Failover protection
- Call analytics

Twilio
0.53 cents/min
- Call recording
- Caller name lookup
- Secure trunking
Benefits of SIP trunking
SIP trunking unlocks numerous benefits for businesses looking to migrate their legacy phone systems to the cloud. These advantages include cost savings, scalability, global reach, and access to advanced cloud features. Here are the benefits of SIP trunk service you should be aware of:
- Cost-savings: As a cloud technology, SIP significantly reduces charges for long-distance calls and physical installations. It follows flexible pricing models — pay-as-you-use pricing and predictable monthly plans — giving you more control over your costs.
- Scalability: In periods of fluctuating call volumes, companies can simply send a request to their SIP provider to adjust their phone lines, avoiding the hassle of manually adding analog lines.
- Flexibility: SIP trunks eliminate the geographical restrictions of traditional PBX, so you can easily obtain phone numbers in any location. Providers offer a unified address for all office devices, ensuring seamless integration of all communication channels.
- Enhanced communications: Besides voice calls, SIP trunking offers a range of communication tools such as video conferencing, instant messaging, and advanced telephony features. It also integrates seamlessly with call center software for efficient management of call volumes.
- Reliability: To ensure business continuity, SIP trunk services offer failover capabilities that direct calls to alternative destinations during system failures or power outages.
Disadvantages of SIP Trunking
SIP trunking also comes with a few limitations that may affect the quality of your phone calls. However, most problems stem from the existing hardware instead of the technology itself. Here are the potential drawbacks to consider before investing in a SIP trunking service:
- Expensive upfront investment: SIP trunking can be resource-intensive as it demands a robust network infrastructure, SIP-compatible PBX, and VoIP-compatible phones. Also, you may need additional cables and maintenance for on-premise setups and outsource support if you don’t have an internal IT team.
- Compatibility issues: Non-PBX devices (e.g., fax machines) and old PBX models previously connected to PSTN lines may encounter compatibility issues when choosing a SIP trunking service. This puts significant pressure on businesses to determine whether their PBX is compatible with the selected provider.
- Good bandwidth is a must: Businesses with weak internet connectivity or teams with heavy data usage may lack the necessary bandwidth to support VoIP calls. Your internet must be robust enough to handle your phone system and data-dependent processes.
Key features of SIP trunking
Switching to SIP trunking opens opportunities to modernize your business phone system. Below are the features that make SIP trunking an excellent choice for businesses seeking to upgrade their traditional phone system:
| SIP trunking feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Call routing | SIP trunking improves call management by offering features that optimize call handling, such as call forwarding, call transfer, and built-in compatibility with interactive voice response (IVR) software. |
| Unified communications | Beyond voice calls, SIP trunking facilitates real-time communication through video conferencing, SMS, instant messaging, and file sharing, moving them to a centralized platform. |
| Call recording and analytics | Track call interactions by reviewing recorded conversations and analyzing data insights based on call usage. |
| Global redundancy | This dynamically routes calls to geographically distributed locations to minimize downtime in case of network failure. |
| Direct inward dialing (DID) | This feature allows incoming calls to be routed directly to a specific extension instead of going through a menu or live operator. |
Choosing the right SIP trunking solution for your business
Finding the right SIP trunking service for your business helps ensure a successful transition from an on-premise system into an internet-enabled phone network. Here are important considerations to factor into your decision when choosing a SIP trunk provider:
- Pricing: SIP providers typically offer two pricing models: pay-per-minute or a fixed monthly rate. Metered pricing is best for businesses with occasional calls, while a monthly plan is ideal for those with consistent usage or high call volumes. Carefully evaluate each option to determine the most cost-effective solution for your needs.
- Compatibility: If you have an existing PBX system, make sure that it is compatible with the SIP technology provided by your ITSP. If not, consider upgrading to an IP-PBX to enable cloud calling. Also, check whether adapters or gateways are required to connect to the SIP service.
- Customer support: The SIP trunking provider must deliver round-the-clock assistance with any network-related issues affecting your SIP trunking service. Ideally, it should offer complete onboarding resources and ensure that clients are guided through the setup process, configuration, and technical troubleshooting.
- Security and reliability: Reliable SIP trunking services should include a clear data policy and robust security protocols to safeguard your company against cyber threats. You’ll also want to check whether the provider has a disaster recovery plan to maintain business continuity in case of outages.
Bottom line
Despite the increasing adoption of cloud-hosted communications solutions, SIP trunking provides a flexible method for businesses that want to retain their legacy phone systems while reaping the benefits of the cloud. If you’re not yet ready to switch to a full cloud phone system, SIP trunking services make a great transitional technology while ensuring cost-savings, reliability, and scalability.
Frequently asked questions (FAQs)
ISDN, which stands for Integrated Services Digital Network, is a legacy technology that uses circuit-switched networks to transmit voice data over physical phone lines (e.g., primary rate interface or PRI). SIP trunking, on the other hand, is a modern alternative to the ISDN, which transmits voice data virtually over an internet connection.
Proper system configuration and adherence to the best security practices are essential for a secure SIP trunking setup. You can start by choosing a SIP trunking service with strong security measures such as encryption, firewalls, and fraud prevention.
A hosted solution refers to a cloud-based phone system managed offsite by a third-party provider, while SIP trunking uses virtual phone lines to connect a company’s on-premise PBX to the internet.
No, VoIP refers to the technology that uses the internet to transmit voice calls, while SIP trunking is a method that allows a PBX system to make and receive calls via the internet without relying on copper phone lines.





