Key takeaways
Being proactive with risk analysis helps set realistic objectives, while creating a complete risk management plan create safeguards against time-consuming and costly oversights. Read on to discover various project risks examples that can emerge during the course of a project, and what to do about them.
Software Spotlight: Wrike
Gain actionable insights through Wrike’s advanced reporting that helps track progress toward strategic goals.
Cost risks
Cost risk refers to the possibility of a project exceeding its allocated budget, a common risk management issue. This financial risk can occur for various reasons such as poor initial budgeting, mid-project scope changes, unforeseen complications, or incorrect cost estimations. Cost overruns can hinder the project’s progress and may stall its completion if the budget cannot be adjusted or supplemented.
How to manage cost risks
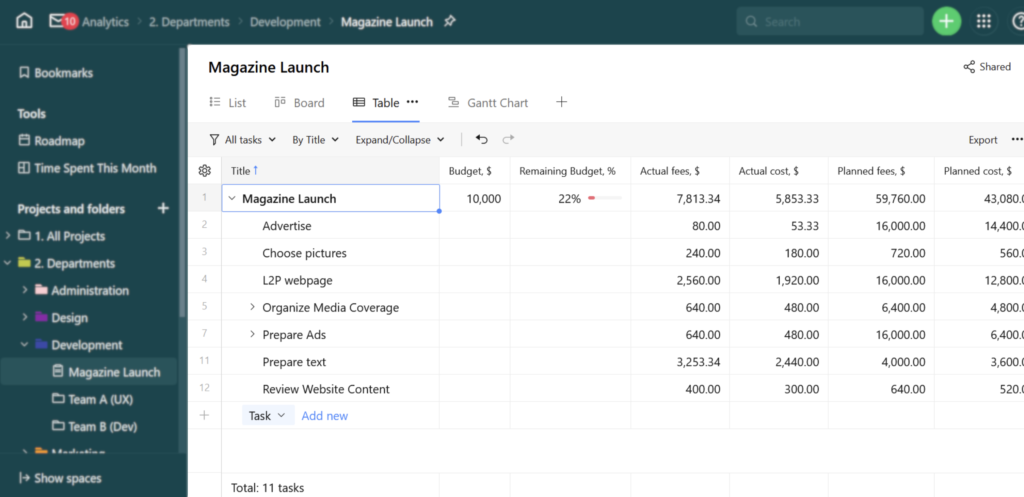
- Use budgeting tools such as those offered by Wrike (Figure F) to set an initial budget and monitor spend throughout the project to prevent overages. Budget management tools are an integral part of risk management processes in several industries. One good example is construction risk management, an industry that often deals with cost issues.
- If possible, set aside a contingency plan or fund so that you have some extra resources on hand in case extra costs arise.
- Revisit vendor contracts and negotiate them or comparison shops to see if you can realize any additional cost savings.
- Conduct regular project risk assessments to identify potential cost overages and create strategies to address them.
Scope creep
Scope risk, or scope creep, refers to the unexpected and uncontrolled expansion of a project’s objectives beyond its original intentions. This risk category typically occurs when project goals aren’t precisely outlined from the start or when requirements change partway through the project.

How to manage scope creep
- Before kicking off a project, take advantage of project scope templates like the ones offered by Smartsheet project management software (Figure A) to create clear expectations and deadlines up front.
- Engage with stakeholders from the very beginning so that all necessary decision makers can help with the creation and the approval of the project scope.
- Schedule regular progress reviews and risk assessments so you can ensure that the initial project scope is being followed and deal with scope creep as it occurs.
Performance risks
Performance risk occurs when a project does not fulfill the expectations and requirements set forth during project planning. Even though a product may have been delivered on time and on budget, that doesn’t guarantee project success, which is the definition of performance risk.
How to manage performance risks
- Identify potential performance hazards from the start of a project by assessing the current market landscape, investigating users’ needs, and staying ahead of technological shifts.
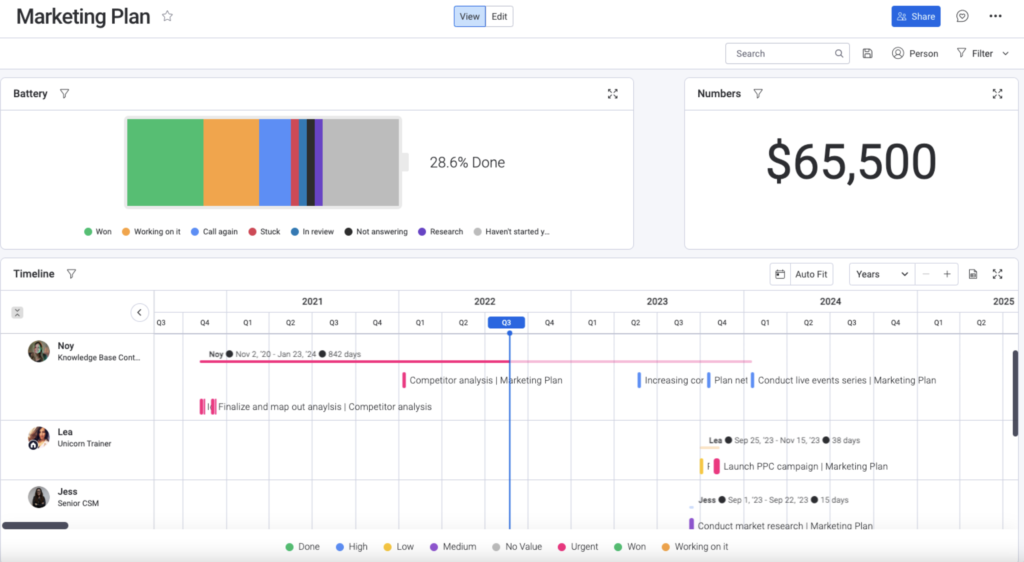
- Use project management software analytics, like this dashboard from monday.com (Figure B), to track project performance and maintain real-time oversight of processes and milestones.
- Foster transparent communication among your project team and conduct regular risk assessments so that performance-related issues can be identified early and often.
External hazard risks
External hazard risk refers to unpredictable events stemming from external factors beyond project management mistakes. These project risks can be natural, such as climate events, or man-made, like vandalism, terrorism, or societal disruptions. These factors can significantly affect the project’s timeline, cost, and quality.
How to manage external hazard risks
- Use historical and political data to regularly asses external risks bases on a project’s locale and nature; enterprise risk management software can be very beneficial for creating these kinds of forecasts.
- Have contingency plans ready, such as alternate work sites or emergency resources, as well as insurance policies to cover potential damages and delays.
- Incorporate practices like safety drills or supply stocking so that your personnel will be safe and prepared in the event of an emergency.
Technology risks
Technology risk covers the potential challenges and threats posed by the hardware and software used to complete the project. These project risks range from technical failures, cyberattacks, and system breaches to the fast-paced evolution of technology itself, including project management software.
How to manage technology risks
- Institute robust cybersecurity measures, including firewalls, encryption, and routine security audits, to fend off cyber threats and technical risk.
- Carefully set roles and permission for your project management software, like the above example in Trello (Figure C).
- Create backup systems and data storage to counteract technical risks, preventing data loss or unplanned downtime, and have a contingency plan in place in case of technological disruptions.
- Conduct regular training sessions to keep personnel updated on new technologies and how to navigate them and on how to prevent cyber attacks.
Operational risks
Operational risk refers to potential disruptions arising from internal processes, people, systems, and project management methodologies. It also encompasses external risk events that impact the day-to-day functioning of a project, such as changes made by vendors or suppliers.
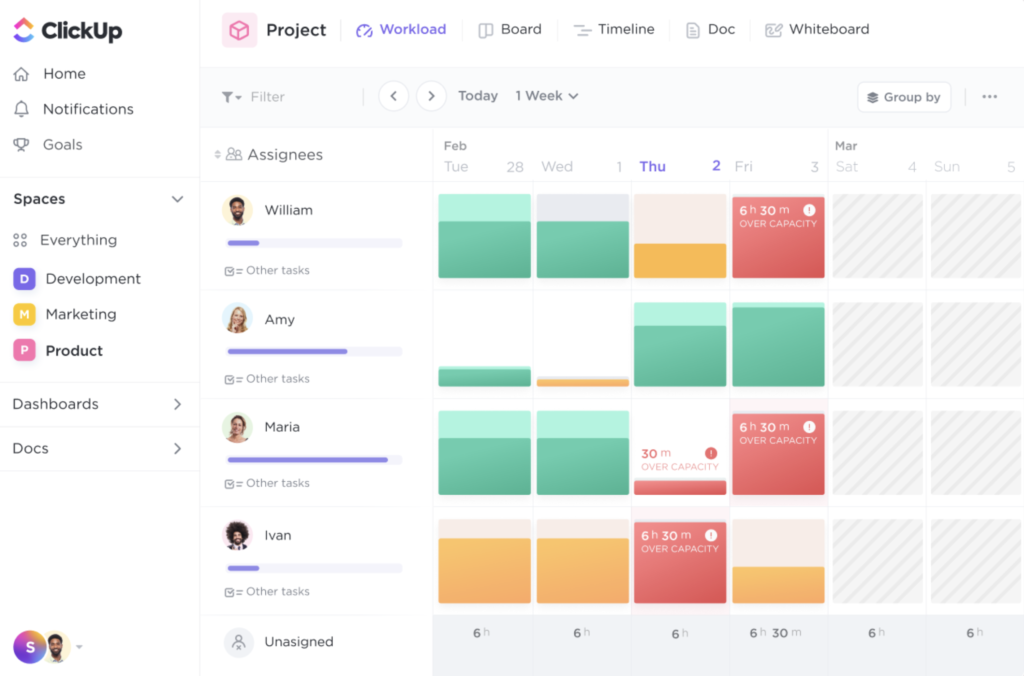
How to manage operational risks
- Use workload management software, such as ClickUp (Figure D), to review workflow and capacity planning and spot operational risks before they arise.
- Ease the transition by ensuring your project team is well-prepared and has time to adjust to major operational changes.
- Consider scheduling regular team meetings to discuss upcoming changes and provide additional training if new processes or systems are introduced.
Communication risks
Miscommunication underlies many project issues, leading to missed deadlines, excess project spend, shifting requirements, uncompleted tasks, and other project management issues. The communication needs to be clear and thorough as well as frequent; if conversations are vague or contradictory, that can cause just as many problems as communicating irregularly or not at all.
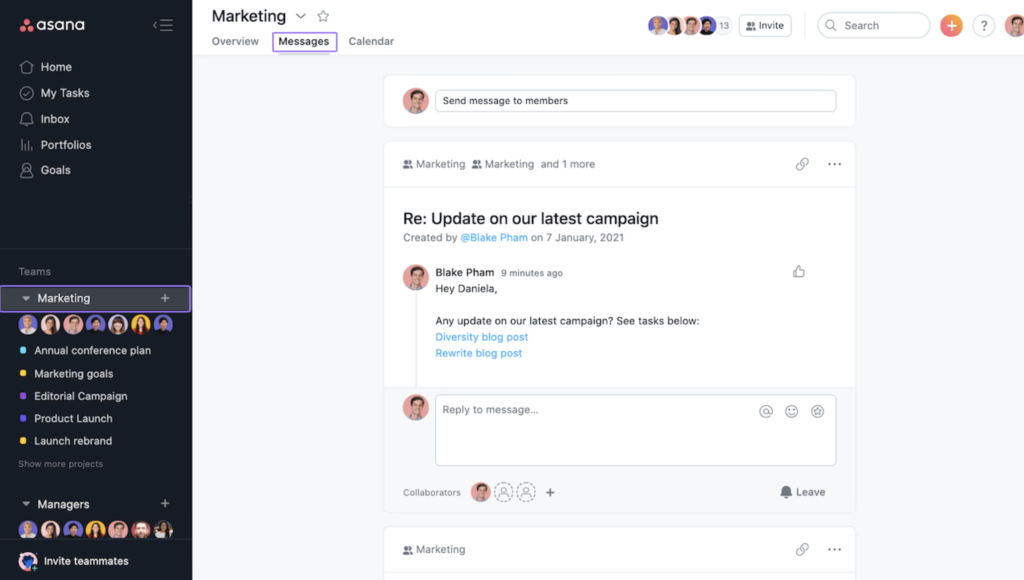
How to manage communication risks
- Utilize a central tool or platform to keep everyone on the same page, like Asana project management software that offers in-app messaging (Figure E), which will help to prevent siloed work.
- Encourage open communication channels so team members can ask questions, seek clarification, and provide feedback.
- Schedule regular meetings with stakeholders and team members to foster collaboration and engage in risk identification.
- Implement strategies to bridge cultural and linguistic differences if the team is diverse.
Skills resource risks
Skills resource risk refers to the potential shortfalls in the necessary skills, expertise, or knowledge among the project team members. Such risks can emerge from a range of factors, from team member turnover to lack of training. This can mean the project management team needs to be more adequately prepared to meet project requirements or handle unexpected challenges.
How to manage skill resource risks
- Assess required skills and compare them with existing team members to pinpoint areas for improvement.
- Invest in training programs that equip team members for specific project demands; a learning management system can help you create custom courses if you can’t find an out-of-the-box one that works.
- Embrace a flexible staffing approach and alternate between permanent and contract roles as needed, especially when niche skills are required.