Key takeaways
One key factor of growing business is expanding to multi channel sales. Retailers, restaurant owners, and service professionals that start transacting in-person would eventually want to reach remote customers to build a wider client base. An ecommerce channel allows these businesses to sell online but would not be complete without having the ability to efficiently and securely accept payments.
What is ecommerce payment processing?
Ecommerce payment processing is the process that allows businesses to accept payments online. It consists of a checkout platform for entering payment details, a payment software that securely sends and receives transaction details between merchants and financial institutions, and the banking service that holds the source of funds for the customer.
Ecommerce payment processing vs. traditional online payment processing
The difference between ecommerce vs traditional payment processing is the payment gateway.
In traditional online payment processing flows, customers are redirected to another site or subdomain to complete the transaction. This third-party payment gateway website, despite being secure, doesn’t make customers feel secure about their purchase and creates opportunities for cart abandonment.
In contrast, the ecommerce payment processing flow integrates the payment gateway service within the seller’s website. This means that once customers click the “Checkout” button, the payment form is hosted within the same site, minimizing the risk of cart abandonment and improving the likelihood of completing the purchase.
Ecommerce payment methods
As with in-person transactions, businesses should provide customers with a variety of payment methods to use online. The availability of options increases the business competitiveness and maximizes sales opportunities. Popular online payments include:
- Credit and debit cards: A line of credit approved by financial institutions and card networks based on an individual or a company’s credit standing. Customers enter their credit card information on an online checkout form.
- Digital Wallets: Digital wallets securely store credit/debit card and banking payment information. Sellers can integrate with digital wallet brands as an alternative to integrating with bank or card networks one-by-one.
- Buy now, pay later (BNPL): BNPL services allow customers to make online purchases on an installment basis, while the seller still receives the payment upfront. There are many BNPL providers and sellers will need a payment integration to offer this payment option.
- Bank transfer: A payment that transfers directly from a customer’s bank to the seller. Online banking can be from an app on a customer’s smartphone or a web-based platform where customers can log in to send payments for an online purchase. The seller’s website will need a payment integration with the customer’s bank.
How does ecommerce payment processing work?
Ecommerce payment processing begins with a combination of key elements. Each one serves a function that contributes to the secure and efficient transmission of transaction and payment information between customer and seller’s financial institutions.
This includes:
Payment gateway
A customer-facing software that provides a platform where customers can enter their payment information. It is connected to the payment processor where the payment sends the data after encryption.
Payment processor
A payment processor serves as the middleman for the customer and the seller’s financial institutions. It provides the technology to process different payment methods and securely send both transaction payment data in the proper format for authentication, authorization, processing, and settlement of online payments.
Merchant account
A merchant account is where the proceeds of the seller’s sales are deposited after transactions are settled. It’s common for merchant account providers to have payment processors as agents in issuing merchant accounts to businesses.
Financial institutions
These are organizations that provide businesses and customers with instruments to initiate transactions as well as approve or deny payments.
- Merchant acquirers: Are banks that approve a business for a merchant account. This comes after the bank evaluates the risk of suffering chargebacks and shut down based on the nature of the business.
- Card issuer: Are banks that approve a customer for a credit card. This also comes after the bank evaluates the risk of a customer’s inability to pay based on their creditworthiness.
- Card networks: Are institutions that provide banks with the ability to approve customers with a credit line to make purchases in-person and online. (Visa, MasterCard, American Express, Discover)
- ACH: An intermediary organization in the US that regulates transactions processed via direct-to-bank deposits such as e checks and ACH debits/credits. Similar financial organizations exist in other countries.
Security and compliance
Ecommerce payment processing adheres to strict standards for handling sensitive payment information. This includes implementing fraud prevention and detection tools, as well as encrypting processed and stored data. The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) for example, is a regulatory body that sets the standards for handling transaction information.
Step-by-step ecommerce payment process
The ecommerce payment process involves the customer, the seller’s website, the website’s payment gateway, and payment processor.
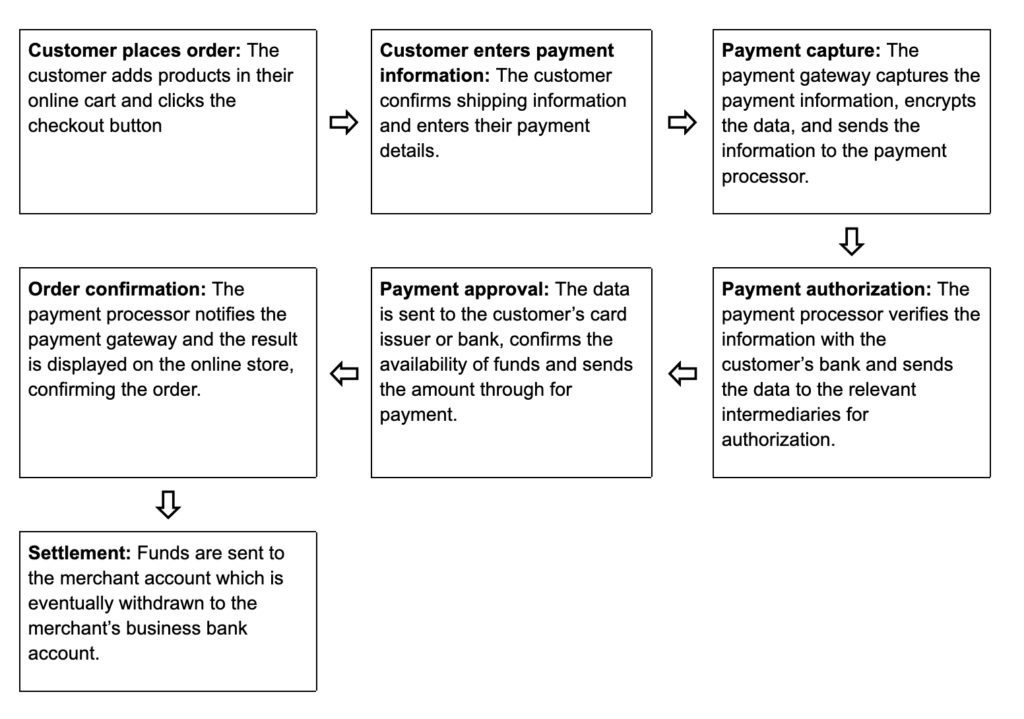
How to choose the best ecommerce payment processor
Not all ecommerce payment processors are built the same so it is up to the business owner to look for a provider that best matches their payment processing needs. That said, there are some common features to look for when choosing an ecommerce payment processor.
PCI compliance
Businesses that accept credit card payment are expected to comply with Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS). This is particularly important when accepting payments online and storing customer payment data for future use. By default businesses have the responsibility to meet this compliance but the best ecommerce payment processors would offer services that relieves the business owner from many of these tasks such as encryption and secure card vaults.
Chargeback management tools
Remote, including ecommerce, payments are riskier than in-person transactions which is why online transaction rates are more expensive. Some ecommerce businesses even struggle getting approved for a merchant account. To mitigate the risk, choose an ecommerce payment processor that offers native chargeback management features, allowing businesses to monitor and promptly respond to chargeback claims.
Variety of payment methods and services
Every business has different payment method requirements based on its target customers’ preferences. As we have listed above, accepting credit card payments is just one option, and the other alternatives offer a combination of options. Payment services such as invoicing, virtual terminal, and subscriptions should also be taken into consideration. Read more: Our picks for top virtual terminal providers.
Value-for-money
The cost of payment processing can take a huge portion of your revenue, so maximizing the features and services you get from an ecommerce payment processor is an important step. Consider a pricing structure that will provide the most savings based on your processing volume and look out for additional costs involved in using payment services that’s most important to earning your revenue. Last but not the least, consider working with an ecommerce payment processor that already provides an ecommerce platform.
Read more: Our recommendations for cheapest credit card payment processors
Ability to grow with your business
Scalability should be a key factor when choosing an ecommerce payment processor. Choose a provider that supports a variety of integrations and developer tools. Ecommerce payment processors that offer low rates and a set of payment plans providing access to advanced customization features may be a better choice than free plans with limited upgrade options.
Top ecommerce payment solutions
Based on the above considerations, the following are our top recommended ecommerce payment processing solutions:

Shopify Payments is the in-house payment processor for Shopify—a leading ecommerce solutions provider. So for businesses still looking for a versatile ecommerce platform, choosing Shopify and Shopify Payments is one of the easiest ways to set up an online business. Shopify offers excellent payment gateway tools such as Shop Pay (one-click payments), advanced shipping, and omnichannel functions. It also has a fully customizable ecommerce set up option for large businesses.
- Monthly fee: $5-$399
- Online payments fee: 2.9% + 30 cents
- Keyed-in fee: 2.9% + 30 cents
- Payment gateway fee: $0
- Virtual terminal fee: $0
- Chargeback fee: $15
- Custom fees: Available for enterprise-level businesses

If what you need is a highly customizable ecommerce payment solution, then Stripe should be at the top of your list. Stripe has been serving advanced online payment processing services long before most popular payment processors. This versatility makes it a highly recommendable payment processor for scaling an ecommerce business. Stripe offers a wide range of customizable online payment solutions for everything from simple ecommerce websites, to marketplaces, even Shopify.
- Monthly fee: $0
- Online payments fee: 2.9% + 30 cents
- Keyed-in fee: 3.4% + 30 cents
- Payment gateway fee: $0
- Virtual terminal fee: $0
- Chargeback fee: $15
- Custom fees: Custom interchange plus fees for large-volume businesses

PayPal is a pioneer in online payment processing and is widely considered as the most trusted name in the industry. This is primarily for its ease of use and powerful technology that brings users a long list of payment options including invoicing and BNPL methods. With millions of customers having a PayPal account, businesses should seriously consider adding PayPal payment methods into their ecommerce payment platform. Remember to add the PayPal logo on your website landing page as it is known to improve sales conversion rates.
- Monthly fee: $0
- Online payments fee: 2.99%+ 49 cents
- Keyed-in fee: 3.4% + 9 cents
- Payment gateway fee: $0
- Virtual terminal fee: $30/month plus 3.09% + 49 cents
- Chargeback fee: $20
- Custom fees: Upgrade to Braintree for custom interchange plus pricing

Small and new businesses looking to add ecommerce to their sales channels can’t go wrong with Square. This provider offers one of the best forever-free POS systems with an all-in-one solution that includes a native website builder and payment processor. Square rivals PayPal in payment methods, offering its own peer-to-peer payment solutions Cash App and Venmo, as well as BNPL via Afterpay. For larger businesses, Square now has a suite of customization options via developer tools and API integrations.
- Monthly fee: $0-$89 (including POS software)
- Online payments fee: 2.9% + 30 cents
- Keyed-in fee: 3.5% + 15 cents
- Payment gateway fee: $0
- Virtual terminal fee: $0
- Chargeback fee: Waived up to $250/month
- Custom fees: For businesses processing more than $250,000 in sales annually, more custom rates and features for enterprise-level businesses
Read more: Check out our top choices for cloud POS and mobile POS solutions.





