Key Takeaways
- The five stages of the adoption curve can be included as milestones or added on a critical path for the five types of employees.
- Including the adoption curve in a project management effort helps the project manager meet expected goals and projected Return on Investment (ROI).
When implementing new Information Technology (IT) software, businesses want to maximize the full potential of the implemented technology on a defined timeline. Personnel can be the biggest hindrance to implementing and using the new technology, and the adoption curve addresses this personnel issue.
ALSO READ: Don’t Let Fear of New Technology Hold Your Business Back
What is the Technology Adoption Curve?
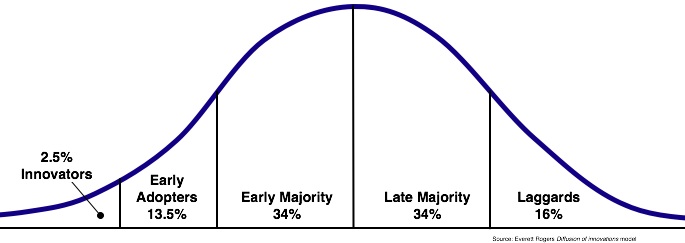
The technology adoption curve uses the bell curve system to categorize five types of employees and how they react to adopting, accepting, and using new kinds of implemented technology in a business environment. The five types of employees are innovators, early adopters, early majority, late majority, and laggards. In addition, each employee type possesses specific characteristics about learning and risk-taking that place them on the left, middle, or right of the technology adoption curve.
How does the Technology Adoption Curve help businesses implement IT changes
Technological progress regularly occurs, allowing businesses to produce their goods and services more efficiently. The technology adoption curve evaluates employees that have a role in using the new technology to ensure an employee’s non-willingness does not impede expected productivity gains to use the technology. In addition, the technology adoption curve helps an organization meet any predefined goals or objectives due to the new technology.
ALSO READ: How Long Should Your Software Implementation Take?
What are the Five Stages of the Technology Adoption Curve
Each employee’s perspective on using new technology is what the adoption curve addresses, and getting an employee to a point where they see the benefits of using the latest technology. An employee understanding the advantage of using the new technology with some degree of motivation to use the new technology is the ultimate goal of the adoption curve.
1. Innovators
Employees who are innovators are ideal for promoting the use of new technology, and they are very motivated to learn. The percentage of innovators is less than three percent, and they are the best advocates for promoting new technology among their peers.
Innovators are considered tech enthusiasts, and they like trying new technology. Innovators are likely to have a personal IT project going on at home. Innovators are the first to upgrade to the latest IT hardware standard or use the newest application. Innovators can tolerate risk, and failing does not intimidate them. Using new and exciting technology far outweighs the risk of failure for innovators. Innovator characteristics are the following:
- Enthusiasm for using new technology
- Willing to tolerate the risk of failure
- Not concerned with the possibility of failing
What motivates the innovators?
Innovators are excited about the opportunity of using the technology. Advertising what the technology can do also motivates the innovator. Kotter’s 8-step change model is an excellent resource to help keep the innovator motivated.
2. Early Adopters
Early adopters are motivated by being the first to know about any new technology. Like the innovators, early adopters are generally younger and not afraid to take risks. Early adopters are considered visionaries. Fourteen percent of employees are considered early adopters, another group of employees that can be advocates for new technology.
The difference between early adopters and innovators is early adopters are concerned about their reputation. Early adopters are very thorough in collecting information from respected sources and documenting their personal experiences with the new technology. After early adopters have validated the latest technology as good, they will support and share the results with their peers. Early adopters’ characteristics are the following:
- Persuasive due to the positive experiences
- Willing participants to work through any issues
- Reputation is important for early adopters
What motivates the early adopters?
Providing the early adopters with how-to and user guide documentation will motivate them. In addition, early adopters are good candidates for doing any beta testing. Finally, once early adopters are comfortable with the new technology, they will help with the organizational change by sharing the results of the technology.
3. Early Majority
The early majority employees are considered pragmatists. The Early majority will test the new technology and look for product reviews to read. The best way to convince this group is to demonstrate the latest technology and how it solves or improves a problem or a process.
Thirty-four percent of employees fall into the early majority group. Employees in this group tend to question the need for change and want to see evidence that the new technology is the best choice. Early majority characteristics are the following:
- Logical
- Practical
- Result-driven
What motivates the early majority?
The early majority is motivated by demonstrating how technology solves a problem. Therefore, this group wants statistical evidence that the new technology is the best solution.
ALSO READ: Setting Expectations for CRM Implementation
4. Late Majority
The Late majority group is similar in two ways with the early majority. First, they make up 34% of the employees who fall into this group, and they are logical. The late majority group will ask questions and quietly observe the implementation of the new technology before they get involved.
Any technology trends do not influence the late majority personnel, and they are hesitant to take any risks. Personnel in this group will delay any software updates and seek peer input from personnel who have applied the latest software update. Late majority characteristics are the following:
- Wary of new technology
- Logical
- Are not risk takers
What motivates the late majority?
The late majority group must see the new technology successfully demonstrated before being motivated. The late majority employees need to see tangible benefits and how the new technology will help them. Once the late majority group sees the technology working, the innovators and early adopters can help answer any lingering questions this group may have. The Late majority personnel are motivated by results.
5. Laggards
Laggard employees comprise 16% of the technology adoption curve, and this group is on the far right of the bell curve. Laggards want everything to remain the same because they are familiar with the tools they are using. Laggards are the stubborn group and are easily frustrated with technology. Laggards want to know what they gain by using the new technology. Laggards’ characteristics are the following:
- Doubtful
- Resistant to change
- Cautious of new technology
What motivates laggards?
Successful demonstration of how the new technology has helped other employees is the best way to motivate laggards. Laggards also need to see documented success from their peers to convince them to use the new technology. With laggards, focus on the benefits and how they are available once they start using the latest technology.
What is a Digital Adoption Platform?
A Digital Adoption Platform (DAP) is a software tool to help new users become familiar with a new software product. New software or a website is embedded within a DAP application, and the DAP provides guidance, critical tasks, and contextual information to expedite the learning process for the user. Digital application platforms are customizable and use AI technology that aids learning.
How does it help a business adopt new IT technology?
Digital application platforms help businesses in multiple ways. For example, the platform lowers user resistance to using new software, increases user satisfaction, provides better insight into what works and does not work, and enhances employee morale.
ALSO READ: Best Practices for CRM Implementation & Training
Managing the Technology Adoption Curve Lifecycle
The technology adoption curve lifecycle is essential enough to be a part of a project management effort for implementing new software. The five stages of the adoption curve can be included as milestones or added on a critical path for the five types of employees. Including the adoption curve in a project management effort helps the project manager meet expected goals and projected Return on Investment (ROI).
Looking for the latest in IT solutions? Check out our IT Software Buyer’s Guide.
FAQs
What is the Technology Adoption Curve?
The technology adoption curve uses the bell curve system to categorize five types of employees and how they react to adopting, accepting, and using new kinds of implemented technology in a business environment.
What are the 5 stages of the Technology Adoption Curve?
Innovators, Early Adopters, Early Majority, Late Majority, Laggards.





