In this article...
What is artificial intelligence (AI) software?
Artificial intelligence software (AI) is virtually everywhere these days. It’s in our homes, we carry it around with us in our pockets, and we sometimes interact with it without even knowing. Businesses use AI to boost productivity in a variety of departments, including customer service, IT security, and marketing. And while some people believe that artificial intelligence will reduce the need for human labor, the reality is that AI will increase the need for skilled workers while reducing the amount of menial labor that humans have to do.
To improve your productivity by implementing AI software in your organization, fill out the survey by clicking on the banner at the bottom of the page. After answering the survey, you’ll get a customized list of vendors that will fit your company’s needs.
Find your new AI software
Compare top AI software 2023
|
Product
|
Chatbots/Virtual Assistants | Data Analytics & Forecasting | Automation |
|
|
yes | no | yes |
|
Astute |
no | yes | yes |
|
|
no | yes | yes |
|
|
no | yes | no |
|
|
no | yes | yes |
|
|
yes | yes | yes |

|
no | yes | yes |

|
yes | yes | yes |

|
yes | no | yes |

|
yes | no | yes |

|
yes | no | yes |

|
no | yes | yes |
Many enterprise software suites now include AI programming, but these tools can be integrated with your existing software to add intelligent agents, deep learning models, or other AI capabilities.
Artificial intelligence, or AI, is a type of computerized model that attempts to mimic human intelligence and is capable of many of the tasks that humans can do. AI machines don’t have brains, and they can’t think in the same way as humans, but they can perceive their surroundings and draw conclusions based on what they see.
Mathematician Alan Turing introduced this segment of computer science when he suggested that machines would be capable of imitating human thought processes. The Turing test, which determines whether or not a machine can pass as a human at least 50 percent of the time, is still used by researchers in AI development today.
What is machine learning?
Machine learning is a subset of artificial intelligence in which the machine uses historical data and linear algebra to inform its future decisions. AI that doesn’t involve machine learning only uses the information it has in front of it right at that moment. Taking this one step further, deep learning attempts to replicate the neural networks found in the human brain to improve learning algorithms.
Explainable AI (XAI) allows users to understand the results that the AI algorithm generates and trust that they are accurate. Researchers use XAI to explain AI techniques.
For now, AI software is fairly limited in what it can do. Most of the tasks assigned to AI revolve around the model ingesting data and then running it through algorithms and logic problems to make predictions or decisions. In the next two sections, we dive a little deeper into what AI tools can and can’t do.
What can AI technology do?
We know AI software improves productivity and lowers operating costs, but what are the actual functions it can handle? This isn’t a complete list, but it at least offers some ideas as to an what AI system can do for your business.
Automate processes
For both digital and physical tasks, AI can automate processes and remove some of the manual labor required to complete projects. These are usually limited to back-end administrative and financial tasks, like updating customer files from email communications, replacing credit cards, or sending invoices to customers. You know, those repetitive tasks that your team spends too much time on? Weak AI can take over those specific tasks and allow employees to focus their attention on more engaging projects.
The kind of AI that automates processes is one of the easiest to implement because there’s generally not much machine learning involved. This type of narrow AI doesn’t need to learn or improve; it just does the job it’s been programmed to do. Business process management software generally takes advantage of these AI models to improve workflows and increase efficiency.
Provide behavioral insights
Wouldn’t it be helpful if you could send marketing emails at the time when your customers were most likely to buy your products? What about detecting strange behavior on your company network? AI capabilities include analyzing user behavior and drawing conclusions based on the patterns it finds. Using this information, you can target ads based on what your customers are interested in, better secure your company data, and even identify fraud as it’s happening.
Not only are these insights typically more detailed than what you’d get from traditional analytics, but as the AI model studies more data, its predictions get more accurate. Deep learning, especially models layered with several neural networks, improves the insights further. Some companies even use this technology during their audit processes to match contracts with invoice numbers and ensure they get everything they pay for.
Engage with customers and employees
Your customers and employees will need help at some point. Unfortunately, your IT team or customer service reps can’t be available all the time. But your AI application can. AI chatbots equipped with deep learning models and deep neural networks can answer technical questions, recommend products, and even make health recommendations based on information already in the system.
For now, more companies are using these chatbots to interact with their employees rather than customers, mainly because they want more control over how they interact with their customers. However, we expect that to change as emerging technology (and the perception of it) improves.
What can’t AI software do?
With all that AI software can do for your company, there are some things that it can’t and shouldn’t be expected to do.
Understand causation vs. correlation
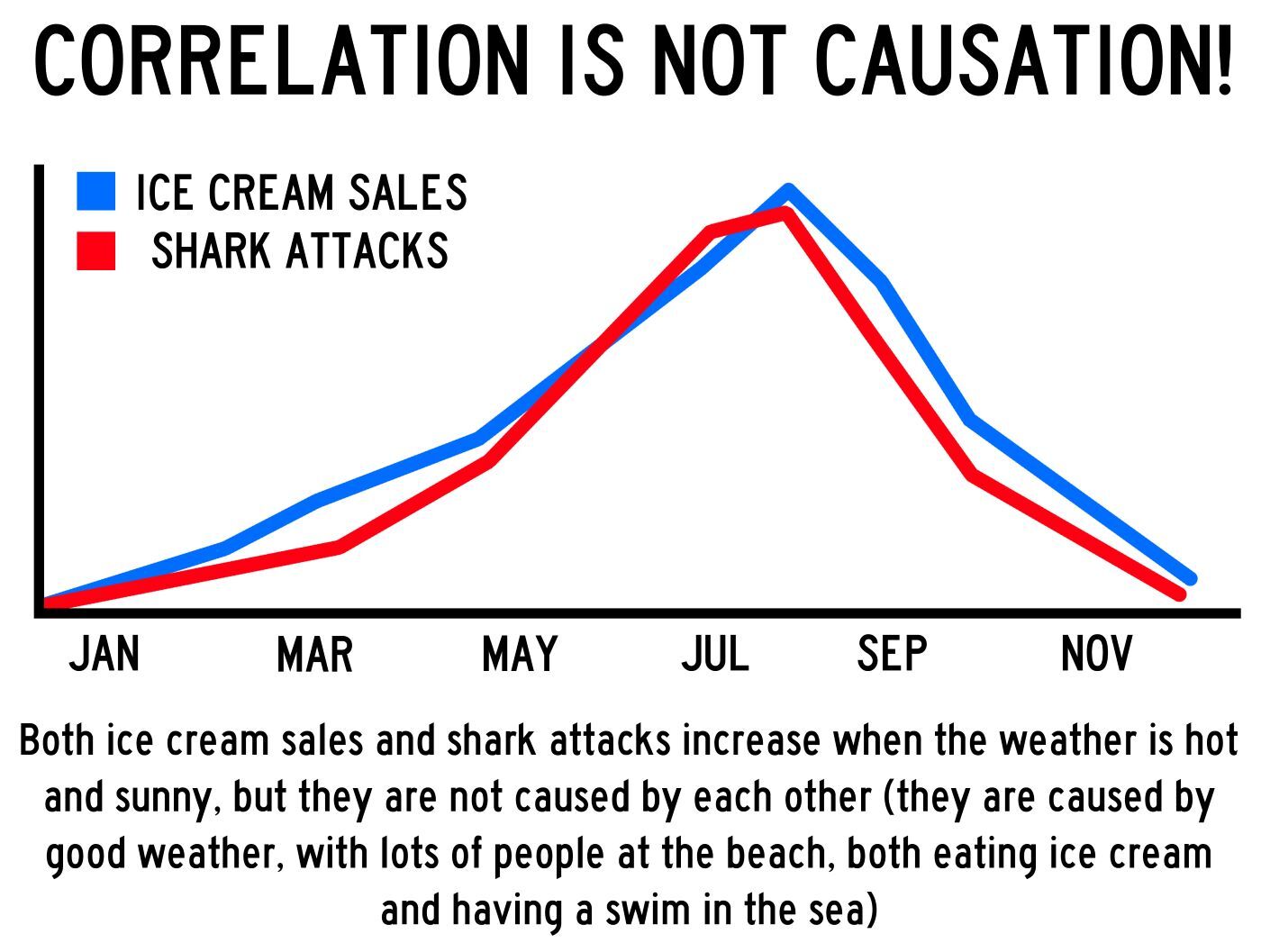
As humans, we can understand that correlation doesn’t always indicate causation. For example, during the months when ice cream sales are highest, the number of shark attacks also increases. We know that sharks aren’t being lured in by ice cream, but even we have difficulty determining what the cause of a trend might be (in this case, it’s likely summer heat).
When artificial intelligence picks up on a trend, it will attempt to connect that pattern to other data it has, leading it to imply causation when it’s really just a strong correlation. This is where human analysis and labor will still be needed. AI can determine which variables seem to have the most impact on others, so this functionality may be on the horizon.
Exercise free will
AI can only perform functions that are within its ruleset. This means it can’t invent, create, or make decisions contrary to what its creator has programmed it to do. AI is still just a computer program, not a brain. It can’t think outside of the limits its programmer has given it. It has to act within the presets and data it has, and it can connect data and form insights very quickly, but it can’t think for itself.
Because AI doesn’t have its own morality or emotions, it doesn’t have desires in the same way humans do. It doesn’t want to solve a problem, although it may be programmed to do so. Until AI research progresses, everything the AI model does is determined by its initial inputs, even if the output is something the original creator didn’t necessarily expect or plan.
Write software or find bugs
Because AI is software in itself, it can’t tell you that there’s something wrong with another piece of software. While it can pick out patterns that may indicate a bug, and many programmers use AI to find those patterns, the program doesn’t know if the new software will work or not without running it. It can’t write new software for the same reason. AI doesn’t have the human understanding of what would solve or cause a problem, so it doesn’t know what code to put together to make the software work.
The four main types of AI software
While many AI programs exist, they can typically be broken down into four main types: reactive machines, limited memory, theory of mind, and self-awareness.
Reactive machines
Reactive machines are one of the most common types of artificial intelligence used today. They’re extremely basic, and they don’t learn, meaning they don’t use past information to influence future decisions. Instead, these are narrow AI models that play humans in chess or use facial recognition in Facebook photos to encourage you to tag friends. Reactive machines cannot improve with time; they simply look at the information currently in front of them and make the best decision they can.
Limited memory
Unlike reactive machines, limited memory models do use machine learning to influence their decisions. These machines learn from the past, either through their own experiences or data that has been fed to them. Basic limited memory machines would have a supervised learning process, also known as reinforcement learning. More advanced models would use unsupervised learning, meaning they wouldn’t need AI researchers to oversee the learning process.
Self-driving cars are an example of limited memory AI. These autonomous vehicles are programmed with the rules of the road, but they also use computer vision to observe other cars and people around them to adjust as necessary to these external factors. Limited memory machines may also take advantage of deep learning.
Theory of mind
Currently, theory of mind is just a concept and hasn’t been completely put into practice quite yet. Artificial intelligence models that fall into the theory of mind category, also called strong AI, would display decision-making ability equal to what human intelligence is capable of.
While voice assistants and chatbots are probably the closest to this category, no AI models are fully capable of holding conversations that are up to human standards. One of the main components of a conversation by human standards is emotional capacity, which up to this point, AI just can’t replicate. The hope is that, eventually, AI will be able to identify and understand emotional behaviors in humans enough to know how to respond to them.
Self-awareness
Self-aware AI doesn’t currently exist, but if it did, it would display human levels of consciousness. Self-aware AI would not only have to be able to identify, understand, and replicate human behaviors, but it would also need the ability to think for itself and have desires or feelings of its own. While current AI is bound by the instructions of its creator, self-aware AI may not have the same limitations.
Common features of AI software
Most AI software types used in business processes have a common set of features to improve productivity and improve the customer experience.
Predictive analytics
Used in sales forecasting, cross-selling, and even content creation, predictive analytics make it easier for your employees to do their jobs. AI systems use machine learning to collect and cross-reference current and historical data to make predictions about the business, including future sales, when a customer is most likely to buy, and even detecting fraud on a business network.
For example, hotels will often use predictive analytics to determine how many guests they’re likely to have on any given day and ensure they’re pricing and advertising rooms adequately to maximize both occupancy and revenue. The AI will take into account local events, seasonal data, and competitor prices to provide actionable insights.
Sentiment analysis
Sentiment analysis is a natural language processing technique that determines whether a statement or series of statements is positive, negative, or neutral. It can also connect emotions to these statements in a basic imitation of human intelligence, both in text analysis and speech recognition. Businesses normally use sentiment analysis to examine their online mentions and determine how their customers feel about their products or services. This allows businesses to find out what makes their customers happy and what they should improve to gain new customers.
Some brands will use sentiment analysis on their social media profiles, so they can find, in real-time, mentions from unhappy customers and respond as quickly as possible.
Multilingual capabilities
It’s pretty unlikely that all of your customers communicate in the same language, and that may also be true of your employees if you’re a multinational corporation. Because of this, your artificial intelligence system should have multilingual capabilities, so both your customers and employees can easily use the program. While this may not be necessary for your organization right now, if you plan on growing, it’s something you should consider.
Workflow automation
Narrow AI models, like reactive machines, can automate repetitive tasks to improve workflows and allow employees to focus their efforts on projects that need their expertise. AI can automatically assign tasks to employees based on their experience and availability to free up more of a manager’s time. Some field service management (FSM) software, like ServiceMax, uses AI to improve scheduling and dispatching. In IT, cybersecurity software uses AI to monitor the network in real-time and flag possible threats, so the security team can spend their time performing investigations and strengthening the network.
Benefits of using AI software by industry
Each industry uses AI software to achieve different goals. Let’s take a look at some of the benefits businesses in different industries get when using an AI program.
Finance
For financial institutions, AI can use predictive analytics to determine how risky prospective loans will be. In fact, credit scores are a form of predictive analytics. Additionally, machine learning capabilities can improve loan underwriting to help reduce risk for the institution. It can also analyze customer transactions to detect fraud more quickly, allowing banks and credit card companies to provide better customer support.
AI software for financial institutions
Mindsay: Mindsay is an AI-empowered chatbot that allows your organization to break from the norm by assisting customers after 5PM, on weekends, and even on holidays. Mindsay helps you lower response times for your customers, increasing their satisfaction. It also reduces the workload on your human customer service agents and frees them up to work on more complex issues, which the software can also route to the correct person. When the AI does need to send a customer to a human agent, it can prioritize issues to make sure customers with the most pressing problems get help first.
InRule: InRule offers automated decision making for financial institutions to improve processes for loan eligibility, fraud detection, and compliance. The AI collects data, including changing market conditions, customer financial data, and financial regulations and uses machine learning to analyze the information to lower risk and increase efficiency. InRule also helps financial institutions provide self-service opportunities to their customers, making it easier for clients to pay bills, request new cards, and monitor their financial activity.
Healthcare
Healthcare teams can combine medical internet of things (IoT) devices and AI to record and analyze patients’ vitals and scans (x-rays, MRIs, etc.) in order to provide care or treatment suggestions. While the technology is not quite ready, eventually AI will offer more at-home health solutions and may even allow surgeons to perform in-home surgeries via robot.
For administrative tasks, AI can improve patient portals and optimize billing procedures, automatically sending invoices, appointment reminders, and insurance requests. Expert systems might even be able to emulate doctors’ expertise for prescription recommendations and similar tasks.
AI software for healthcare providers
Astute: Astute gathers real-time data and combines it with information from customer surveys to provide insights to patient experience and how you can improve it. It also provides conversational chatbots that allow you to improve your patient portal and assist customers 24/7. Using Astute, you can reduce some of the strain on your administrative staff, automating tedious processes like billing, emailing appointment reminders, and processing insurance claims. The software can read and interpret relevant documents, so your staff doesn’t have to.
Alteryx: Alteryx helps you determine the best healthcare offerings by analyzing the needs of your local population, and improves your forecasting to ensure you have enough staff on hand for seasonal peaks. The AI can also evaluate your pharmacy and physician partners to ensure you’re referring your clients to providers with the best quality of service and pricing. Alteryx also takes healthcare regulations into account to ensure any decisions are compliant, while also analyzing financial and operational risks associated with policy changes.
Manufacturing
In the manufacturing industry, AI can automate certain aspects of production to improve workflows and minimize strain on employees. With inventory control, supply chain managers can set minimum product thresholds, and if the inventory dips below that level, the AI can automatically place new orders.
Additionally, machine learning can improve forecasting capabilities, so managers can decide how much of a product they need to produce in each run. It can also identify bottlenecks in production, allowing managers to stagger breaks to keep a machine running if necessary.
AI software for manufacturing companies
RapidMiner: RapidMiner helps manufacturing companies improve their efficiency through more accurate forecasting and optimized supply chains. The software identifies product defects quickly to reduce waste and liability. Using RapidMiner, you can also predict maintenance needs and address them proactively, saving money on machine repairs. And to make products and support better, you can collect and analyze customer feedback to get actionable insights.
IBM Watson: IBM Watson adds artificial intelligence to pre-built applications from IBM, making it easier to incorporate AI into your supply chain if you already use IBM software or are thinking about switching to it. The software aggregates data from siloed systems and provides forecasts and insights to improve supply chain efficiency. The collection of data gives you great visibility across your entire supply chain and helps you mitigate potential disruptions before they happen. The AI is already trained on supply chain language, cutting down your implementation time and improving time to value.
Marketing
AI enables marketers to better personalize their communications with customers, increasing engagement and conversion rates. AI software can analyze consumer profiles and tailor product recommendations based on previous browsing habits or purchase history.
Marketing automation is also a big help in improving a brand’s engagement. Marketers can set up email sequences that automatically filter recipients into different campaigns or paths depending on the actions they take. The marketer simply sets up this campaign once and then the AI runs it for all of the recipients that get put into the funnel, saving them time and freeing them up to work on other campaigns.
AI software for marketing teams
Blueshift: Blueshift uses predictive AI models to determine when customers are most likely to engage to deliver the right messages at the right time. It can also help you decide which channel is right for your content to improve customer engagement. The AI offers predictive scoring which you can measure against results to better train the software and make sure it’s using the right data. You can also pull products directly from catalogs to improve your messaging.
Salesforce Einstein: While you do have to have Salesforce to use it, Salesforce Einstein offers customer insights based on their past interactions with your company to improve engagement and conversion rates. The software improves employee efficiency by providing them recommendations for the best next steps. It also improves customer service by reducing response times and providing a more personalized experience through smart chatbots.
Real Estate
For real estate agents, AI can improve lead management and help them identify their ideal clients. For example, agents who specialize in high-end homes could use AI to pre-qualify potential customers and ensure they can afford that type of home before contacting them.
AI is also improving real estate for home buyers. Home search tools like Zillow allow buyers to input their ideal home characteristics, and the software provides a list of homes that meet that criteria. However, AI can take this one step further by examining buyers’ browsing history to determine their preferences and put houses that best match those preferences at the top of the list.
AI software for real estate agents
Luma Digital Labor Product Suite: Luma Digital Labor Product Suite frees up real estate agents’ time by providing their clients with a self-service option for easy questions. Realtors can use it individually, or agencies can use the platform to qualify leads and connect them to agents that meet their needs. The suite includes a virtual assistant equipped with natural language processing, knowledge base, and workflow automation platform all powered by AI for increased efficiency.
Roof AI: Roof AI is an AI-powered chatbot that helps real estate agents convert serious leads into customers with quick, automated responses directly on their website. The platform answers client questions in real-time and helps them through the home buying process. With Roof AI, realtors can improve their client experience and lower their response times without dropping everything for their customers. The software can also send personalized content to your clients to keep them engaged throughout the process.
Retail
The retail industry can benefit from AI through chatbots that allow their customers to contact them any time day or night. Customers get quick answers to questions which improves their perception of the brand. Additionally, with AI handling simple questions like “where is my order?” or “what is your return policy?”, customer service representatives are free to answer more complicated questions or handle disgruntled customers.
Along with improving customer service, e-commerce retailers can use AI to upsell their customers with tailored product recommendations. When a customer adds an item to their cart, you can show them items related to that product that they might also like, increasing the value of each sale.
AI software for retail businesses
SmartAction: SmartAction provides retail businesses with smart chatbots that answer customers’ simple questions or route complicated situations to the right human agents. With natural language processing and sentiment analysis, the software can understand customers’ needs and either help them on the spot or provide context to the agents that will assist them. To free up employees’ time, the AI can handle inquiries about points balances, billing, order tracking, and updating profile information.
Competera: Competera is an AI solution built to help retailers improve their pricing models and data science to improve profitability. The software performs competitive product analysis to see how your products measure against competitors’ and helps you improve and price them accordingly. It can automate and optimize pricing, backing up its decisions with cause and effect analysis for price changes and demand patterns. It also analyzes similar products across regions, taking into account different currencies and languages.
AI software has many uses, so finding the right one for your business can get a little tricky. Companies in the retail industry or that have customer support departments would benefit from AI-enabled chatbots to improve the speed of their response times. Sales teams and manufacturers need AI software with robust forecasting capabilities and machine learning. Whatever your company needs, there’s likely a form of AI software that can make it easier.





